Demonstration of Research
Hybrid stereo audio source separation combining directional clustering and supervised nonnegative matrix factorization with spectrogram restoration
Almost all music signals are produced as a stereo format with the left and right channels. The stereo signals are typically applied "stereo effect," which gives differences of volume, timbre, and timing between the channels. In particular, the difference in volume (often called panning) is essential to create spatial directions for each source.
On the basis of this volume difference, we can easily separate such directions, e.g., left, center, and right directions. This technique is called "directional clustering" and can be achieved by clustering each time-frequency components using volume ratio.
In directional clustering, each component in the time-frequency domain is clustered into the left, center, and right directions, and binary (0 or 1) mask matrices of each direction are estimated. Since this process is a simple clustering problem, directional clustering does not require any prior information or training. However, the sound quality of the separated sound is degraded because the binary masking causes artificial distortion. In addition, sources in the same direction cannot be separated.
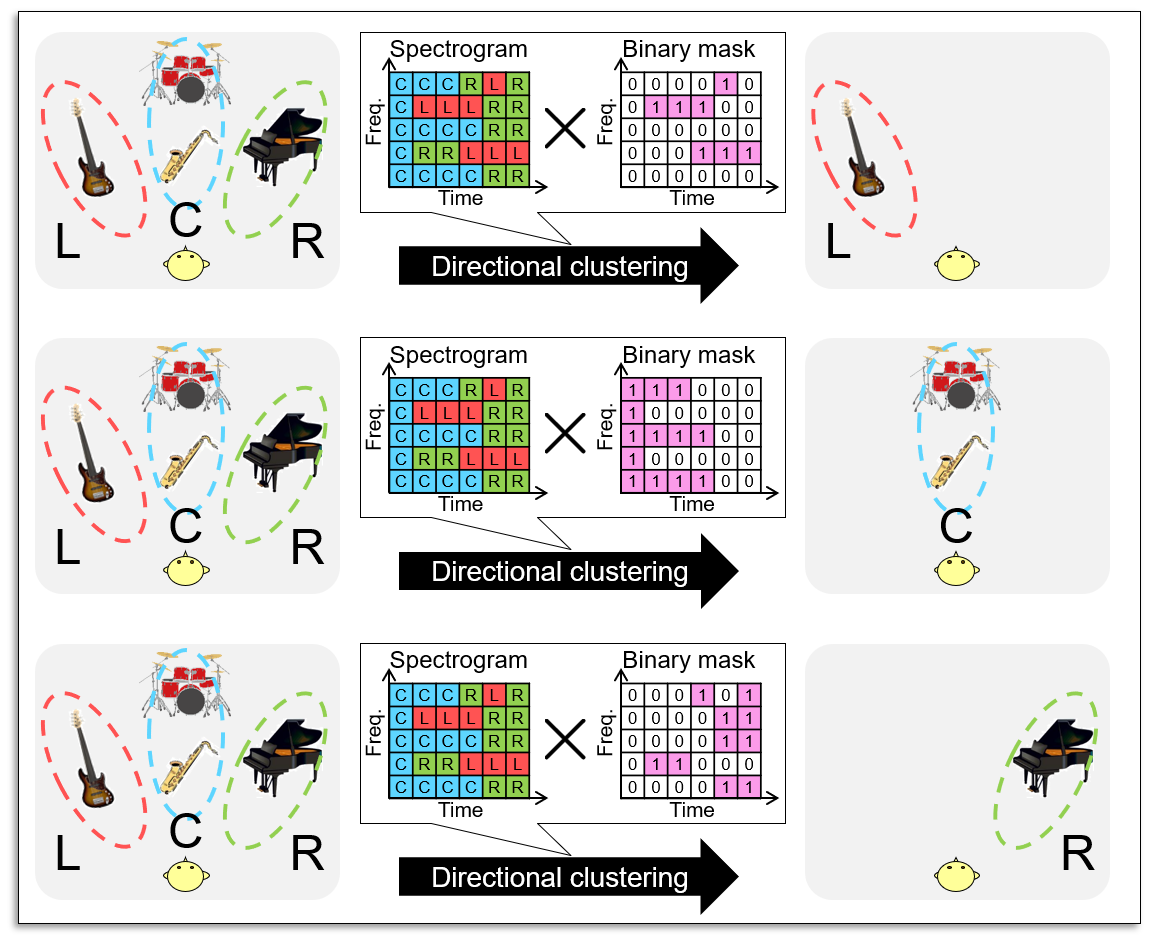
The degradation of sound quality in directional clustering is due to the inaccurate estimation of the binary mask matrix. The misestimation of the binary mask will cause a lack of components (spectral holes) in the target direction, which results in artificial distortion.
To solve the quality-degradation problem and separate sources in the same direction, we proposed a new algorithm called "supervised NMF (SNMF) with spectrogram restoration" (see here for SNMF). The entire algorithm is called "hybrid stereo audio source separation," which combines directional clustering and SNMF with spectrogram restoration.
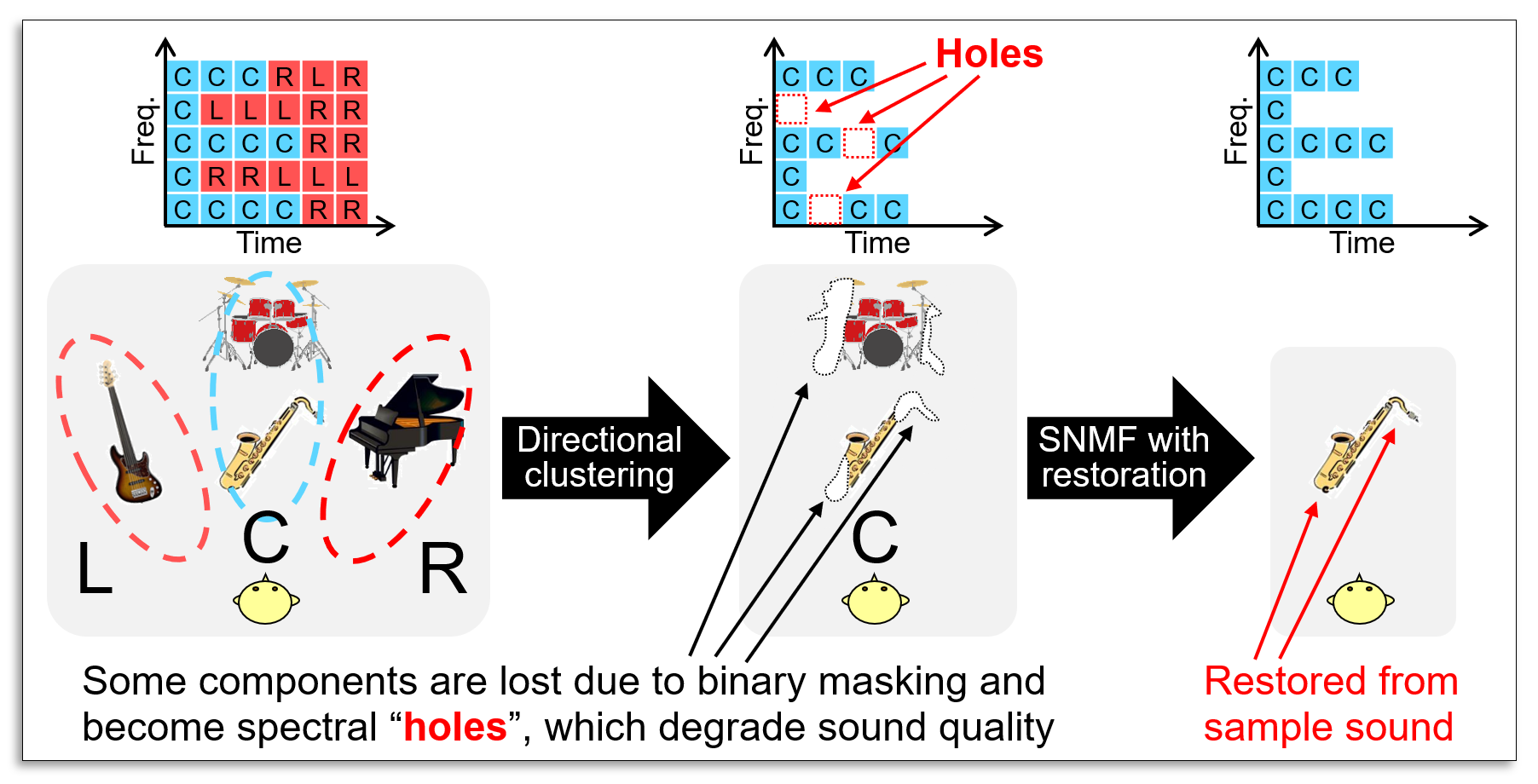
In SNMF with spectrogram restoration, the lost components are ignored from a cost function in SNMF. Since SNMF utilizes timbre parts trained in advance using a sample sound, the lost components are extrapolated using them, and the sound quality of the separated signal is restored.
The following demonstration separates the stereo music signal by the hybrid stereo audio source separation, where we used a two-octave (24 notes) sample sound of the target source. Although the output sound of directional clustering includes much distortion, the following SNMF with spectrogram restoration restores its sound quality and separates the residual interference.
Separation of stereo music with four sources
(Piano, Guitar, Bass, Drums)
Separated result of directional clustering (1st stage)
(Drums)
(Piano, Bass)
(Guitar)
SNMF with spectrogram restoration (2nd stage)
(input signal is center direction)
(two-octave Piano notes)
(Piano)
(two-octave Bass notes)
(Bass)
References
- Superresolution-based supervised NMF with time-continuous regularization
-
- D. Kitamura, H. Saruwatari, K. Shikano, K. Kondo, and Y. Takahashi, "Regularized superresolution-based binaural signal separation with nonnegative matrix factorization," Proc. 3DSA, 2013.
- Stereo audio source separation using superresolution-based supervised NMF
-
- D. Kitamura, H. Saruwatari, Y. Iwao, K. Shikano, K. Kondo, and Y. Takahashi, "Superresolution-based stereo signal separation via supervised nonnegative matrix factorization," Proc. DSP, 2013.
- Online divergence switching for superresolution-based supervised NMF
-
- D. Kitamura, H. Saruwatari, S. Nakamura, Y. Takahashi, K. Kondo, and H. Kameoka, "Online divergence switching for superresolution-based nonnegative matrix factorization," Proc. NCSP, pp. 485–488, 2014.
- Optimization of divergence for supervised NMF with spectrogram restoration
-
- D. Kitamura, H. Saruwatari, S. Nakamura, Y. Takahashi, K. Kondo, and H. Kameoka, "Divergence optimization in nonnegative matrix factorization with spectrogram restoration for multichannel signal separation," Proc. HSCMA, pp. 92–96, 2014.
- Hybrid stereo audio source separation combining directional clustering and supervised NMF with spectrogram restoration
-
- D. Kitamura, H. Saruwatari, S. Nakamura, Y. Takahashi, K. Kondo, and H. Kameoka, "Hybrid multichannel signal separation using supervised nonnegative matrix factorization with spectrogram restoration," Proc. APSIPA ASC, 2014.
- D. Kitamura, H. Saruwatari, H. Kameoka, Y. Takahashi, K. Kondo, and S. Nakamura, "Multichannel signal separation combining directional clustering and nonnegative matrix factorization with spectrogram restoration," IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio, Speech, and Lang. Process., vol. 23, no. 4, pp. 654–669, 2015.